Do You Need Carbs for Muscle Gain?
Muscles are the organ of longevity. Unfortunately, most people ignore its critical role in health.
Having muscles means living longer.
Some are worried that on a carnivore diet all their gains will disappear.
“Eat carbs,” they say, “they’re essential”.
But do you really need carbohydrates for muscle gain? The short answer is no.
The long answer is, well… I’m about to give it to you.
Why Build Muscle?
You may believe that muscle is all superficial and eating healthily is sufficient.
This could not be further from the truth. To build muscle mass means to build longevity. To not build muscle mass means to increase your likelihood of mortality by twice.
Specifically, people with low muscle mass have twice the rate of mortality as those with high muscle mass, as indicated by the study below.
The reason for this is simple: muscle helps prevent chronic disease.
How so?
1. Building muscle and exercising increases bone density: Bone strength is essential for long term health. The largest loads on your bones come from muscle contractions. Skeletal muscle mass tends to correlate with bone strength.
2. Muscle increases mitochondria volume: Aging is linked to mitochondria dysfunction, potentially as a result of volume reductions. The study below showed that exercise increased mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and mitochondrial volume.
3. Muscle increases insulin sensitivity: Disruption of the normal uptake of glucose by muscles is central to the progression of diabetes. Muscle sucks up excess glucose for storage as glycogen.
4. Muscle improves cancer survival rates: Patients receiving therapy for lung cancer had worse survival rates with lower muscle mass.
5. Muscle protects against injury: 50% of women older than 65 years old who break a hip in a fall never walk again. Muscles can help prevent and protect you against damage from falls.
6. Muscle loss reduces quality of life: Sarcopenia, muscle loss with aging, significantly reduces quality of life and can lead to institutionalization.
7. Muscle prevents obesity: Muscle increases metabolic energy expenditure. Every 10-kg difference in lean mass increases energy expenditure by 100kcal / day.
Abstaining from building muscle can be significantly debilitating in the long run. If you’re in your 30s and not building muscle, you’re losing it. If you’re losing muscle, you’re shortening your life.
Move forward, not backward. Get your ass to the gym.
How to Build Muscle
Muscle growth requires three things, none of which are carbohydrates.
1. Resistance Training and Exercise
Muscle growth starts with resistance training.
Muscle size gain results from a delicate balance between protein synthesis and protein breakdown. When you stimulate your muscles you cause changes in its myofibers, which ultimately leads to increases in the size and quantity of protein fibers in the muscle.
Scientists believe cells called “satellite cells”, precursors to muscle cells that are turned on by exercise, mediate this process:
“Once aroused, satellite cells proliferate and ultimately fuse to existing cells or among themselves to create new myofibers, providing the precursors needed for repair and subsequent growth of new muscle tissue”
Muscle size gain is controlled by three mechanisms:
Mechanical Tension: The force and stretch that creates mechanical tension are essential to muscle growth.
Damage: Exercise results in localized damage to muscle tissue. In response, your body creates inflammation around the site. Macrophages remove debris and growth hormones are released, rebuilding the muscle even stronger.
Damage tells your body that it must grow stronger for the next time it conducts the same activity. Scientists believe this is the biggest reason for hypertrophic gains.
Metabolic stress: Metabolic stress has been shown to increase hypertrophic response. Anaerobic glycolysis builds up metabolites like lactate and creatine. This changes the hormonal environment, induces cellular swelling, and increases sympathetic nerve activity and growth oriented transcription factors.
How you decide to build muscle may vary. So as long as your muscle is stressed to failure, muscle gain can occur with or without weights.
If you are not ready to toss around heavy barbells, you can still get all the benefits from bodyweight training.
For instance, this study showed that training at lighter weights for more sets & reps may actually produce greater muscle growth than 1 set to failure.
No excuses.
Even in the on-demand world we live in, there’s no button you can press to gain muscle.
There’s a reason most people are not strong. You need to put in the work. Start resistance training.
2. MTOR Activation
Muscle mass is regulated by the balance between protein synthesis and breakdown. mTOR is a kinase that plays a vital role in anabolism and catabolism. You can think of it like an on / off switch for cellular growth:
“mTOR is a serine/threonine kinase which senses various environmental and intracellular changes including nutrient availability and energy status, and coordinates diverse cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, autophagy, survival, and metabolism”
To build muscle, you need to activate mTOR. It controls all signaling that ultimately leads to the growth or destruction of muscle mass.
Two ways to activate mTOR are:
Resistance Training: As this study shows, single bouts of resistance exercise may activate mTOR for greater than 24 hours.
Nutrients: Ingesting certain foods and amino acids activates mTOR. Leucine is the primary driver of mTOR activation. It is found in copious quantities in beef liver (which is why I think beef liver is better than any protein shake). Growth factors, energy status and oxygen can also activate mTOR1, but leucine remains the most potent activator.
3. Amino Acid Intake
Amino acids are the building blocks for protein. Ingesting protein and amino acids is necessary for the hypertrophic muscle response.
The two main determinants of muscle mass gain are hypertrophic activity and nutrient availability. Amino acids are oxidized and lost from muscle cells and are necessary for repair and growth.
Your body cannot endogenously create all of the amino acid building blocks you need. Thus, amino acids are an “essential” part of your diet.
There are 9 essential amino acids: histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine.
Most nutritional and workout supplements treat protein as 1 single macro nutrient. But this crude metric distracts away from the value each individual amino acid provides.
Instead of treating protein as a single nutrient, it is better to treat each amino acid as a single nutrient. In this way, amino acids are much more akin to micronutrients than they are to carbohydrates or fat.
Amino acids vary in their digestibility. They are also very important for muscle stimulation.
The DIAAS score is the best measure of the amino acid content and digestibility of proteins.
Sources of Amino Acids
Muscle meats and animal products are a great and complete source of amino acids for muscle mass. Leucine, which is prevalent in animal products such as beef liver, is one of the most potent stimulators of mTOR. According to Dr. Stuart Phillips:
“Leucine is the king AA, it turns on the anabolic signalling pathways and initiates muscle protein synthesis (MPS) by activating mTORC1 Once leucine has ‘switched on’ muscle protein synthesis (MPS) then this process proceeds for a relatively short period of time (1-2h) until it is switched off”
Animal foods are the most complete and bioavailable source of protein.
Reading a protein powder label obviously won’t tell you this.
Not all foods have equally digestible amino acids. Many foods, especially vegetables, contain antinutrients (i.e. tannins, phytates, trypsin inhibitors), which block protein absorption.
Just because a vegetable is quoted as having substantial amounts of proteins doesn’t mean you can absorb all of it.
Building Muscle on Keto: Carbohydrates Are Not Necessary
Do you need carbs for muscle gain?
Insulin and Insulin-Growth-Factor can also activate mTOR. Carbs stimulate insulin, so people have long assumed they are required for muscle growth.
This is a common misconception. Carbs are anything but necessary for mTOR activation.
Resistance training coupled with sufficient protein and leucine intake will activate mTOR independent of carbohydrate intake.
As this study showed, Leucine can activate mTOR independent of insulin.It also found that insulin was not accretive to muscle growth, independent of protein.
“What of a role for insulin in regulating anabolic responses to nutrition (via nutrient-induced secretion)? While it is noteworthy that provision of protein alone (i.e. without carbohydrate) causes a rise in insulin similar to that seen following a mixed meal (Atherton et al. 2010), insulin apparently does not contribute to the anabolic effects of EAAs on MPS. To exemplify this, EAA infusates robustly stimulate MPS even when insulin is ‘clamped’ at postabsorptive concentration”
Another study found that resistance training can activate mTOR even without IGF activation.
And if these two observations were not enough to convince you, this study tested whether 50 g of carbohydrates post exercise would increase muscle synthesis.
When you have adequate protein intake, adding 50 g of carbs does not increase muscle protein synthesis whatsoever.
The myth that carbohydrates are necessary for muscle gain has been dispelled. You can stop eating carbs now.
Exercise Without Carbs Improves Performance
If anything, exercising without carbohydrates has been shown to be beneficial. In a randomized group of cross fit athletes, those on keto:
Lost 7.6 lbs more
Lost 2.6% more body fat
Lost 6lbs of fat mass
Improved their overall cross fit performance
What About Muscle Glycogen?
The theory around muscle glycogen is also commonly misunderstood. Muscle glycogen — stored glucose — provides size and energy for performance training. As such, many have assumed their bodies need exogenous glucose to replenish these stores.
What they have failed to understand is their bodies can create glucose endogenously by breaking down protein and fat molecules.
This study by Jeff Volek et al pictured below found that endurance athletes on the ketogenic diet had the same glycogen stores as those eating carbohydrates.
Do not fall for the propaganda. Hunter-gatherers were active.
More active than most people today. They weren’t refueling with Gatorade powders and pasta dinners. They were refueling with animal fat and protein-heavy diets.
Carnivore Diet Is The Best Muscle Building Diet
To recap, there are three pieces to the muscle building puzzle:
Resistance training
mTOR activation
Amino Acids
On a dietary level, the carnivore diet is perfect for all three and if done correctly, will give you olympic-level strength (check out Dr. Shawn Baker or Jerry Texeira).
The Carnivore Diet is High in Bioavailable Protein and Amino Acids
As we discussed, adequate protein intake is necessary for muscle gain.
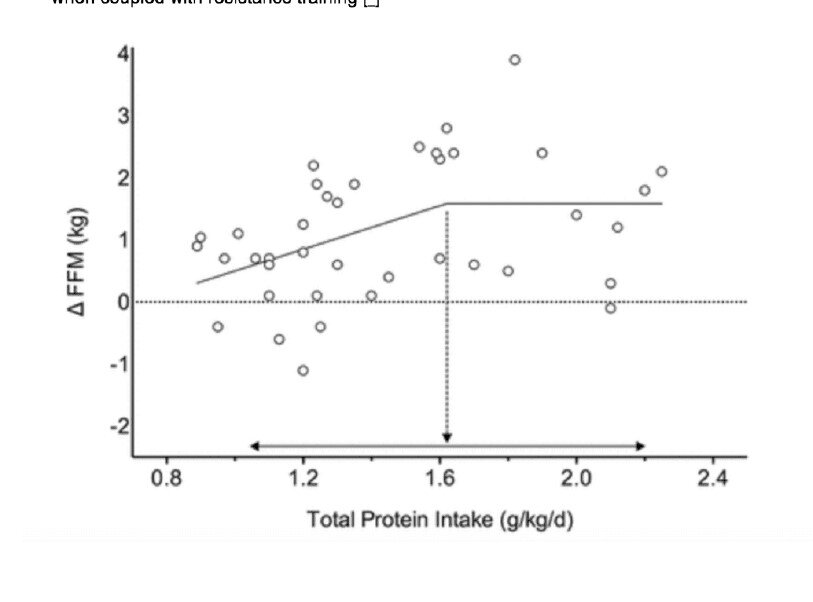
The RDA is woefully deficient in protein. Dr Stuart Phillips has shown that at a daily intake of at least 1.6g of protein / kg of body weight up to 2.2g of protein / kg of body weight is optimal for muscle synthesis.
As the graph below illustrates, at least 1.6g / kg level is critical for lean mass gain. Data from 49 studies showed that protein supplementation significantly increased strength and muscle size when coupled with resistance training.
Additionally, other studies have suggested the importance of having protein with every meal throughout the day.
This study found that frequently consuming meals with 30g+ of protein increased muscle mass.
The carnivore diet centers each and every meal around protein and will ensure that muscle protein synthesis is maximized.
Not All Protein Is Created Equal
Not all protein is created equal. Veggie based protein is not a substitute for animal protein. Proteins in animal products are more bioavailable than plant based proteins.
– Out of 21 g of protein from beef, 14 g are complete
– Out of 22 g of protein from beans, 0 g are complete
16 oz of ribeye has 108 g of protein. If you weigh 160 lbs, a 16 oz ribeye would get you to almost 90% of the recommended daily protein intake..
Plants will detract from your performance. Steak and liver will augment it.
Steak is Better Than Protein Shakes
Instead of using nutritionally devoid, toxic waste like Muscle Milk, eat steak.
Muscle milk and many protein shakes are loaded with sugars, carbs, seed oils and four syllable toxins that have no place in our vocabulary, let alone our diet.
And it’s all for just 20g of protein.
Eating steak and liver post-workout will get you more bioavailable protein, without all the negative side effects.
The Carnivore Diet is High in BCAAs & Leucine
Leucine is a key trigger for muscle protein synthesis. Getting at least 2 g post workout is optimal.
“We estimate that a protein/AA source containing ∼1.8–2.0 g leucine would be sufficient to activate a postexercise “leucine trigger” due to the exercise-induced AA flux and/or improved muscle sensitivity to AAs. Leucine plays a key role in the postexercise MPS response, at least when total protein intake is lower.”
The carnivore diet provides a complete amino acid profile, high in leucine. Beef liver is one of the best sources of leucine. The foods highest in leucine are all animal products
Ketones Improve Performance
One last study conducted by Jeff Volek showed that ketones improved performance.
In this study, twenty six college men were divided into two groups: one group was on a keto diet and the other on a traditional western diet. Each group worked out three times a week.
What happened? The ketogenic diet group gained 4.3 kg of lean muscle mass while the traditional western diet gained 2.2 kg of lean muscle mass. The ketogenic group also lost 2.2 kg of fat while the western diet group lost 1.5 kg of fat.
On the carnivore diet, your ketones will be elevated. And so will your performance.
Conclusion
The evidence is clear. Building muscle is the result of resistance training and adequate nutrient intake. Low carb is the best diet for performance and carbohydrates are hindering your muscle gain.
The best way to build muscle while maintaining a low and healthy body fat % is a combination of the carnivore diet and exercise.
Most people are doing the exact opposite. They’re loading themselves with toxins just to get bigger.
Wake up. Take back control. Unlearn everything you’ve been taught about nutrition. Eat steak and liver. Workout hard. You will feel stronger than ever.
This article was originally published at www.carnivoreaurelius.com.